In December 2021, the Japanese robotics company Gitai was testing its R1 rover, which was commissioned by Jaxa and intended to travel to the moon. A video released a few months later makes it possible to appreciate the device’s capabilities under realistic conditions that recreate the properties of the lunar regolith.
In parallel with the Artemis project, some space agencies are preparing with rovers for their next visit to the moon. This is the case Japanese Space Agency Specialized in collaboration with a Japanese company Robotics, Gita. In September 2020, Jaxa announced that it was working with a private company to design. Robots Allocated to carry out missions in space.
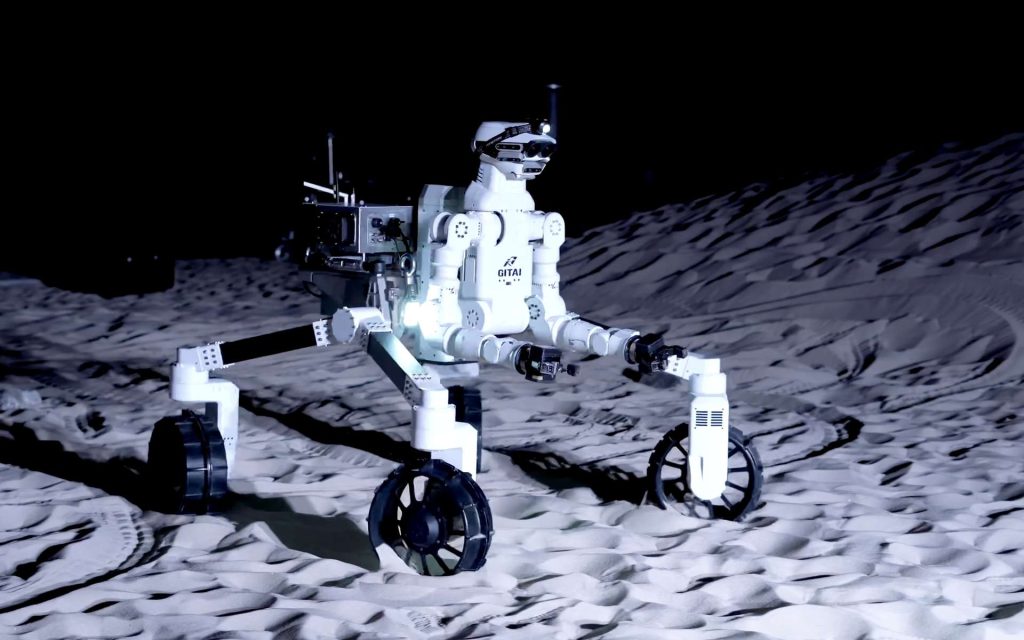
For this purpose, Gitai has developed a multifunction rover called R1. In December 2021, R1’s capabilities were tested under realistic conditions, on the surface reflecting the Moon’s plain and its specifications. In a video released in February 2022, the robot impresses with its fluidity and its capabilities. The rover can thus easily maneuver and change direction, overcoming natural obstacles or even collecting objects on the ground. The test took place at the Sakamihara campus in Japan.
The technology is amazing
The R1 is equipped with four legs, whose wheels, in many directions, allow the rover to quickly change its position. Testing demonstrates that the unit can overcome medium-sized obstacles and rocks when raising or lowering the rover’s trunk. Thanks to its mobility, it can climb even at rated slopes of 15 to 20 degrees.
The two obvious weapons placed on the front of the robot make it possible to carry out regolith collection operations on the ground. Grippers positioned at the end of the hands can be used to drop lunar dust samples into a container using a small spade, which is then sealed by the rover before storing it in a container. The arms, split into several parts, give R1 a wide range of motion. Controlled remotely by an engineer, the device makes precise and technical gestures: it can easily separate a bar from a set, move it, and use tools. Gitai expresses its knowledge by building its rover A contact relay And a set of solar panels. R1 executes precisely the movements required for the assembly of the structure by screwing the support or adjusting the position of the solar panels.
Is R1 more efficient than man?
The collaboration established between Jaxa and Gitai aims to democratize robotic travel to space and the moon. L ‘Japanese Space Agency Wants to oversee operations at low financial cost, with robots operating efficiently where humans cannot move. On his site WebsiteThe Japanese company expresses its ambition: Participate in the construction of lunar bases And Mars in the early 2040s and beyond.
For the R1 rover, the impressive technological demonstration of December 2021 should confirm the Japanese space administration in its ambition for robotic missions to the moon. Under the rover’s video presentation, the Gita points out that the latter could quickly make its first turns in lunar dust by 2025.
Special Offer: For Father’s Day, Offer the Best Science!
Your father is great Science enthusiast And unusual discoveries? If you give it to him Fantastic scientific study In paper form? Benefit -20% In Mac Futura (Special offer: Instead of € 15 19): 220 pages to explore 4 scientific issues that will shape our future!
Mag Futura:
- 4 major science questions for 2022, from Earth to Moon
- 220 pages, 60 experts: No fake news, just science
- Home delivery with electronic gift card
- An independent scientific medium
Are you interested in reading now?

“Avid writer. Subtly charming alcohol fanatic. Total twitter junkie. Coffee enthusiast. Proud gamer. Web aficionado. Music advocate. Zombie lover. Reader.”










More Stories
Acrylic Nails for the Modern Professional: Balancing Style and Practicality
The Majestic Journey of the African Spurred Tortoise: A Guide to Care and Habitat
Choosing Between a Russian and a Greek Tortoise: What You Need to Know