Venus is suddenly interesting again. After planetary research focused on the Moon and Mars in recent years, it is now back to Venus. The U.S. space agency NASA wants to send two probes there, as it did on Wednesday (local time) Communication. German researchers will also be involved in a mission.
This result is no surprise. Last autumn, scientists discovered phosphine molecules in the planet’s atmosphere, which was interpreted as a strong indication of microbial life. This observation is strong among experts Controversial.
Nevertheless, then-NASA executive Jim Friedenstein announced in September that it was “time to prioritize Venus.” Prior to that, it was unnoticed by NASA: the last U.S. mission to closely monitor the planet in 1978. The Soviet Union stayed for a long time, and Isa explored the planet with the “Venus Express” from 2006 to 2014.
Like the earth and as different as hell
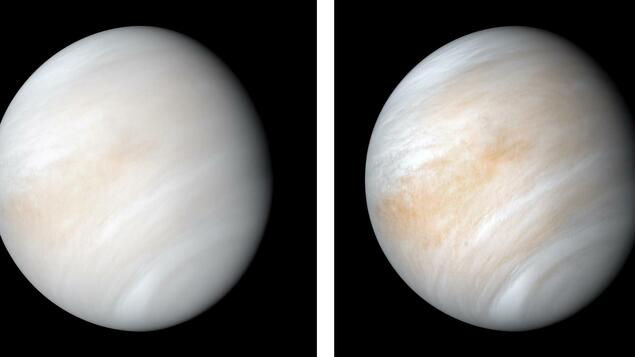
Venus is considered the sister planet of Earth. It is similar in size, but its orbit is closer to the sun. This is hospitality in Venus. It is surrounded by dense clouds of sulfuric acid, which have a strong greenhouse effect: the surface temperature is 460 செல் C, and the liquid water evaporates instantly. In addition, the air pressure is almost a hundred times higher than on Earth. This corresponds approximately to conditions at a depth of one kilometer.
Compared to the Moon and Mars, Venus is more complex for research tasks because the studies have to be much stronger. Accordingly, little is known. In ancient times, when it was still cold, the planet had an ocean. There are those who are still active today Volcano.
Two new NASA missions are aimed at understanding “how Venus became a hellish world capable of melting lead on the surface,” NASA’s new head Bill Nelson said Wednesday. Both have a budget of $ 500 million (4 410 million) each and are scheduled to launch from 2028 to 2030.
Once upon a time there were oceans on Venus?
One is called “Da Vinci +” (the deep atmospheric Venus inquiry into noble gases, chemistry and imaging). It is necessary to determine the composition of the atmosphere by using a probe to travel the ground through the clouds. Researchers hope to decipher how the atmosphere was created and created and whether there really was an ocean. In addition, the study should provide accurate images Terrain structures Create, which is considered a sign of plate tectonics.
The other study, known as “Veritas” (Venus emissivity, radio science, incarnation, topography and spectroscopy) will not land, but will orbit Venus for five years. Since the cloud cover does not allow light waves of visible spectrum to pass through, a normal photo camera will not see anything. But waves of other frequencies can pass through – and they are recorded to get images of the surface: near the radar and infrared range.
Researchers hope that the radar images will provide an accurate 3D landscape model that can answer their questions about volcanic and plate tectonics. Infrared data is collected by an instrument developed at the German Space Center (DLR) Berlin Institute of Planetary Research. Jorn Helbert of DLR said, “With this, we can identify whether there is a volcano or not. Infrared data show heat on the one hand, but also the chemical composition of the surface.
Young volcanic eruptions differ from older ones – like the Earth, where volcanic “basalt” basalts occur, and older continents have an “acidic” granitic crust. The DLR tool VEM (Venus Emissivity Mapper) will generate a global map showing the different types of rocks. But first it has to be fixed with Venus: hot rocks emit different wavelengths than cold. In Helbert’s laboratory, several rock samples have already been brought to the Venus heat and measured so that VEM data can be accurately interpreted.
Completely different rules of the biological game in space?
“It’s hard to say whether life really exists,” says the researcher. There are different interpretations for phosphine measurements. “They are all consistent with existing data. This shows how little we know about Venus. ”This fact, therefore, may have prompted Helbert and Naveen to deal with Da Vinci + and Veritas.
More trips may follow. Created the concept of IsaEnvision is scheduled to launch in 2032. Early next week, Helbert says the decision can be made. The US company plans to do this by 2023 Rocket Laboratory Start a study to find traces of life in the upper layers of the atmosphere, the company’s boss Peter Beck announced in 2020.
The Bremen space agency OHP has also been promoting missions to Venus for a long time. “To find out if there are completely different rules of biological play in space, is there life that arises only from sunlight?” In my view such a task is fully justified“OHB boss Marco Fuchs, who argued at the end of 2019.
“These findings will be very helpful in better estimating the life probabilities of thousands of foreign aircraft.” Provided that there were sufficient donors for such efforts.

“Avid writer. Subtly charming alcohol fanatic. Total twitter junkie. Coffee enthusiast. Proud gamer. Web aficionado. Music advocate. Zombie lover. Reader.”










More Stories
Acrylic Nails for the Modern Professional: Balancing Style and Practicality
The Majestic Journey of the African Spurred Tortoise: A Guide to Care and Habitat
Choosing Between a Russian and a Greek Tortoise: What You Need to Know